Signs Your Posture Is Draining Your Workday Energy
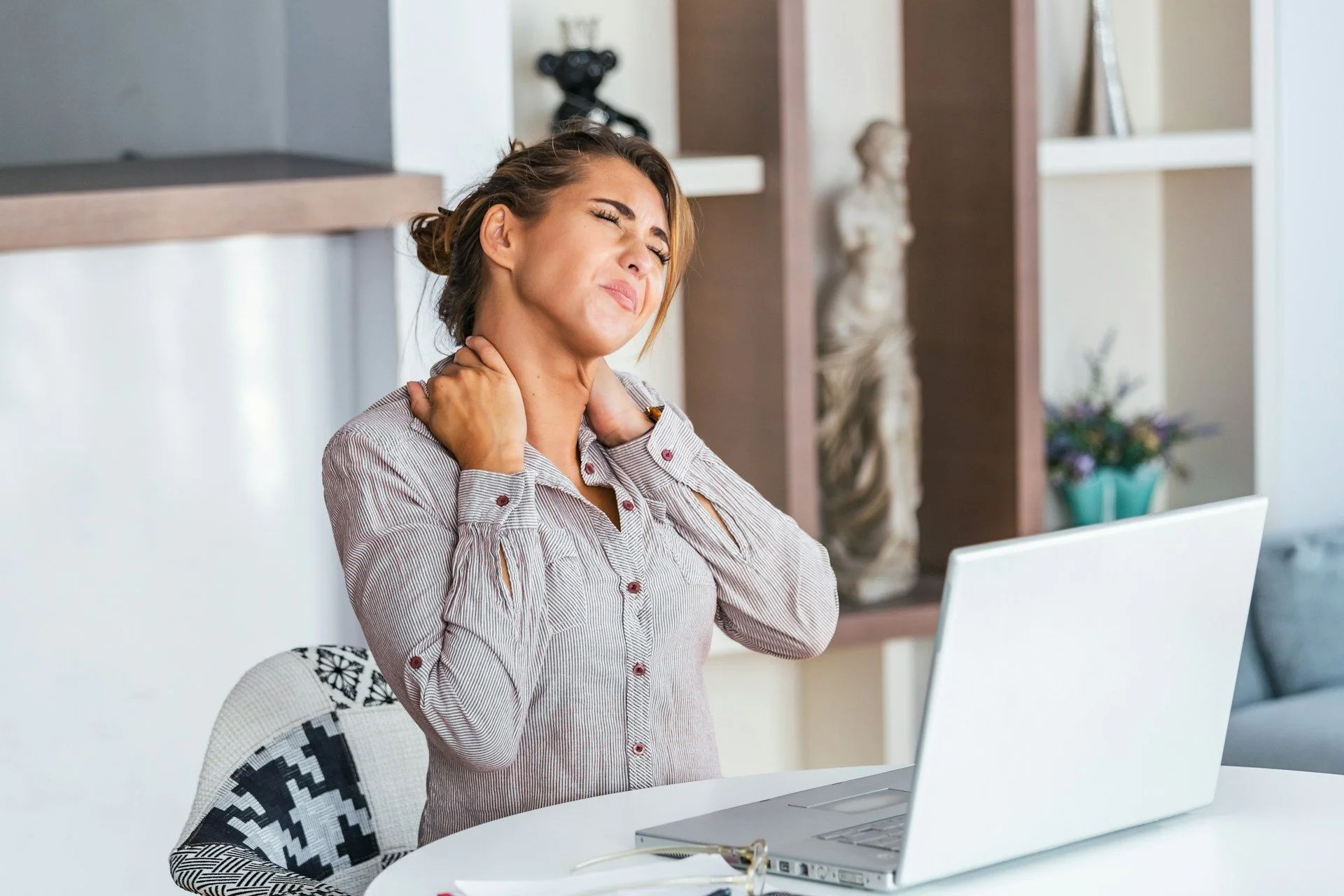
Posture is about far more than sitting up straight. The way you hold your body while you work changes how your spine and nervous system manage load, attention, and stress. If your posture is working against you, your energy can fade long before your to-do list does.
As the year gets moving again, many people go from holiday mode straight back into long desk days, full inboxes, and warm afternoons. Your nervous system is already juggling deadlines, family life, and the heat. Add hours of slumped sitting or craning toward a screen, and it is no surprise that focus and stamina can drop.
Subtle posture habits often drain energy long before clear pain shows up. That afternoon fog, that sense of being wired but tired, or that dull neck tightness can be early messages from your body. When we catch these signs early, we can protect performance, not just react when something finally hurts enough to stop work.
At Align Chiropractic in South Melbourne, we work with people who want their bodies and brains pulling in the same direction across pain, prevention, and performance. A chiropractor for posture problems can help you understand how your spine and nervous system are coping with your work demands, and what might support you better.
Subtle Energy Red Flags Most Professionals Ignore
Many professionals dismiss their tiredness as poor sleep or too much coffee, when posture is quietly involved. Some common red flags include:
• Afternoon brain fog that creeps in around the same time each day
• Reaching for extra caffeine just to stay sharp in meetings
• Feeling wired but tired after back-to-back calls
• Having less mental bandwidth for complex decisions by mid-afternoon
Sustained forward head posture, rounded shoulders, and a slumped lower back increase load on your spine and the muscles that support it. This can strain your neck and upper back, but it also asks more effort from your breathing muscles and nervous system. Even if there is no sharp pain, running your body in this mode all day can feel like working with the handbrake partly on.
Try a few simple self checks during your workday:
• Notice how your body feels after a long video call
• Pay attention to the depth and ease of your breathing while you type
• See if you always lean on the same elbow or perch on the front edge of your chair
• Observe whether your chin drifts toward the screen without you realising
These are not reasons for alarm. They are signals that your system is under load. The goal is not to chase perfect textbook posture, but to build more supportive patterns that match your real work life.
How Posture Shapes Focus, Mood, and Stress Resilience
Posture changes the messages your spine sends to your brain. When your spine is heavily loaded or stuck in one position, the feedback going into your nervous system shifts. This can influence your ability to concentrate, regulate mood, and respond to stress at work.
A collapsed or rounded posture often comes with shallow breathing. The ribcage does not move well, the diaphragm does not work as freely, and neck muscles try to help with each breath. Over time, this can mean:
• Less efficient oxygen delivery
• A greater sense of mental fatigue
• More effort just to stay focused through long tasks
This can be especially noticeable on hot afternoons or during long strategy days where you sit for hours. Many people describe feeling mentally flat, even if they slept well.
More efficient posture supports clearer thinking and a steadier mood. When your spine moves well, your breathing is easier, and your nervous system can adapt more easily to stress and change. For people in high-stakes decision-making roles, this can be the difference between coping and feeling constantly on edge.
A values-led chiropractor for posture problems will look well beyond clicking a sore back. Care is about how your spine and nervous system are coordinating movement, load, and recovery across your whole week, not just what happens at the desk.
Physical Clues Your Posture Is Costing You Performance
Your body often gives physical hints that your posture is costing you extra energy. Some common clues include:
• Recurring neck or shoulder tightness by late morning
• Tension headaches after screen-heavy days
• Jaw clenching during emails or meetings
• Feeling stiff and slow when you stand up after long sessions
Asymmetries are another sign to notice. You might see or feel:
• One shoulder sitting higher than the other
• Your head tilting slightly to one side in photos
• An uneven feeling in your pelvis or hips when you sit
• One leg you always cross over the other
These patterns change how efficiently you move, which can change how much energy you spend just holding yourself up. You might find it hard to stay comfortable in one position for more than 20 to 30 minutes, or need to constantly shift and cross your legs. Some people feel unusually drained after driving or commuting, even if the distance is short.
None of this means your body is faulty or broken. It could mean that there are patterns that can be assessed and supported. Sometimes that involves working with a chiropractor for posture problems.
Small Daily Shifts That Protect Your Workday Energy
You do not need a complete workstation overhaul to make a difference. Often, small, realistic changes made consistently can help your body cope better with long days.
Helpful daily shifts can include:
• Taking micro breaks every 30 to 45 minutes, even for 30 seconds
• Standing up between meetings instead of scrolling emails
• Alternating between sitting and standing if your set up allows
• Doing a brief movement reset when you return from the bathroom or kitchen
Simple posture-focused habits can also help:
• Set your screen so the top is around eye height
• Bring your keyboard and mouse close so your shoulders can relax
• Use your chair backrest to support a gentle, neutral curve in your spine
• Notice when your chin drifts toward the screen and bring it back in line with your chest
Because your nervous system is at the centre of this, strategies that support it matter too. Gentle breathing drills, such as slow nasal breathing with relaxed shoulders, can take pressure off your neck. Short walking meetings, where practical, can reset both your body and your brain. You might also use daily transitions, like coffee runs or phone calls, as cues to change posture rather than staying frozen at the desk.
The aim is sustainable posture and energy that fits your late summer work rhythm, not rigid rules you cannot keep. Small, consistent adjustments usually beat big dramatic changes that only last a week.
When to Seek Individual Support for Posture and Energy
Self-management is often a good starting point. But there are times when getting personalised help makes sense. Consider seeking support if you notice:
• Persistent fatigue even after making lifestyle tweaks
• Recurrent headaches, neck pain, or nagging tightness
• Tingling, numbness, or referred pain into the arms or head
• A clear drop in your usual performance or focus at work
At Align Chiropractic, an evidence-informed, function-first assessment may include a detailed health and work history, movement and posture analysis, and neurological checks. The focus is on clear explanations, a detailed plan with ongoing progress assessments, so you understand what is happening and what your options are. We collaborate well with GPs, physios, and other health professionals, and any care plan is shaped around your goals, whether that is getting through the day with less fatigue or supporting high-level performance over the long term.
For professionals in South Melbourne and surrounding areas, it can be helpful to ask a simple question: is my current posture and energy level in line with the kind of year I want to have at work and at home? If the answer is no, the next step may be exploring how tailored chiropractic care could fit into your broader self-care and performance strategy.
Start Improving Your Posture And Comfort Today
If you are noticing stiffness, fatigue or recurring aches from sitting or standing, a tailored plan with our chiropractors for posture problems can help you move more comfortably. At Align Chiropractic we assess how your body is functioning day to day, then guide you with specific adjustments and practical posture strategies. Whether you are at a desk, on your feet or juggling both, we focus on realistic changes that fit your routine. If you are ready to get started or have questions about your situation, contact us today.
Guide to Family Chiropractic Support at Every Life Stage
Families don’t stand still. From newborn naps to teen sport injuries, and everything in between, our bodies shift and stretch with the way life unfolds. Often, those physical changes can show up in the form of tension, soreness, or discomfort, sometimes gradually, sometimes all at once. That’s why it makes sense to think about how care fits into different life stages.
Family chiropractic care is one way to look at the bigger picture. It takes into account not just one person’s aches or habits, but how growing, moving, and living together shapes physical well-being. In this guide, we’ll walk through a few common points where families may notice changes in how they feel, and how paying attention during those times can make daily life more comfortable.
Support for Young Children and Toddlers
When babies start crawling, walking, and exploring their world, their bodies are adapting quickly. Most of the time, things go smoothly, but even small bumps and falls can stack up over time. As toddlers grow, they move a lot, sleep in all kinds of positions, and sometimes end up in a heap at the bottom of the lounge after tumbling off. These are all small moments, but they can lead to patterns.
Posture in kids starts forming earlier than most people realise. Long stretches of time in prams, car seats, or watching screens with heads bent forward may gently shape the way they move and hold themselves later on. These habits don’t always seem like a big deal, but when combined with growth spurts, they can create tension in joints or muscles.
Gentle approaches work best at this stage. Kids don’t need heavy-handed care, they need light and thoughtful guidance that suits their stage of development. When we check how their bodies are moving, we’re looking mostly for how to help them feel easy and balanced as they grow.
Child and adolescent chiropractic checks are a big part of our practice at Align Chiropractic, focusing on comfort and restoring movement for younger family members, especially after falls or growth spurts.
Helping School-Aged Kids and Teenagers Stay Active
By the time school starts, kids are often spending more hours sitting than moving. Desks and backpacks become part of the daily rhythm, and for active kids, sport brings a whole different set of physical bumps. It’s a big shift from early primary through to adolescence, with quick growth often adding extra stress on bones, muscles, and posture.
• Heavy schoolbags and long classroom days can pull the neck and shoulders forward
• Growth spurts can throw balance off or put strain on the spine
• Tech use, like phones, gaming, or laptops, can create habits that stick without realising
These changes don’t always show symptoms straight away. One day, a child may mention a sore neck or headaches during class, and it can feel like it appeared out of nowhere. That’s when regular check-ups can help spot small imbalances before they settle in.
When Parents Are the Ones Feeling It
Caring for others is a full-body task. Whether it's lifting heavy toddlers, standing all day at work, or sitting too long in front of a screen, parents often carry their own set of physical stress without noticing until it starts to hurt. Usually, it shows up as a tight lower back, aching neck, or dull headaches that come and go.
The added pressure of broken sleep, early mornings, and after-school runs means recovery time is limited. If we don’t take a moment to look after our own bodies, that tension builds bit by bit. And while energy might be aimed at helping others, it’s much harder to do that when the body is saying it needs a break too.
Family chiropractic care isn’t only for kids. Parents benefit when support is balanced across the whole household. We take time to look at posture, joint movement, and patterns that build over weeks and months. That way, small adjustments can make daily life feel more manageable.
Staying Mobile and Comfortable Through the Later Years
As we age, the way our bodies respond to everyday strain starts to shift. Movements that felt easy in our 30s or 40s might suddenly feel tight, or recovery after a bump or fall might take longer than expected. That’s normal, but it doesn’t mean we should ignore it.
Common experiences in the later years include:
• Stiffness in the lower back or neck after waking or sitting
• Changes in posture, sometimes feeling more hunched or unbalanced
• Slower healing from everyday strain or joint fatigue
These changes can leave people feeling cautious or uncomfortable when staying active. But movement is still important, especially when done in ways that feel steady and safe. That’s where support focused on comfort and mobility can really help. Gentle care can offer a soft nudge to movement patterns, helping older adults stay steady without overloading the system.
For seniors, Align Chiropractic provides gentle care that focuses on keeping movement easy and supporting independence, with respect for each person’s health history.
Why It’s Worth Checking In at Different Life Moments
No matter the age, our bodies are always shifting. Some of those shifts are obvious, like kids growing out of shoes overnight, but others are more subtle. Tension can build quietly in the background, and it’s often not until something snaps, clicks, or strains that we realise how long it’s been creeping up.
That’s why it makes sense to pause from time to time and really check in. We may notice little aches that come and go, or spots that feel stuck or irritated more often than before. When care is shaped around the whole family, each person's support can match where they are now, not where they used to be five years ago.
Staying Comfortable Together as Life Changes
We all move at our own pace, yet our lives are connected. Whether it’s a child adjusting to a new term or a grandparent recovering from summer activities, bodies respond to the rhythm of everyday life. Back pain, headaches, and posture changes don’t always come with a warning, but they often share a cause.
When a household pays attention to those changes as a group, it’s easier to notice patterns. One person might start feeling better with a small switch in daily habits, and that can ripple across the rest of the family. Staying aware and staying open means daily routines can feel smoother, and comfort becomes something that we all share, not just something we chase after when something goes wrong.
At Align Chiropractic, we understand that each stage of family life brings unique challenges, both physically and emotionally. Listening to your body and noticing changes early can help stop minor discomfort from becoming a persistent issue. Whether you're running a busy household or just starting to feel the signs of tension, we're here with supportive care tailored to your needs. To discover how family chiropractic care could benefit you and your loved ones, contact us to get started.
How a Chiropractor Helps Sciatica from Long Summer Drives
Long summer drives can be a great way to enjoy the warm weather, take a break, or visit family and friends. But spending hours in the car often means sitting still in the same position for way too long. If that sounds familiar, and you’ve noticed back pain shooting down your leg afterwards, you could be feeling the effects of sciatica.
That kind of discomfort isn’t unusual during the holidays or road trips. It's the sort of pain that comes on gradually or suddenly, and it can hang around longer than you'd like. If this sounds like something you've experienced, speaking with a chiropractor for sciatica might help you understand what’s going on and why it keeps happening. Let's look at why summer driving can trigger these symptoms and how some support might ease the pressure.
What Sciatica Feels Like and Why It Happens
Sciatica happens when the sciatic nerve, one of the longest nerves in your body, gets irritated. That nerve runs from your lower back, through your hip, and down the back of each leg. When something pressures the nerve, such as a tight muscle or spinal joint irritation, it can cause pain or strange sensations down one side of your body.
• The pain can feel sharp or shooting, and it might get worse with sitting or standing too long.
• Some people feel tingling, burning, or even numbness in parts of their leg or foot.
• Others notice weakness when moving the leg or foot, especially after being in the same spot too long.
For many, sitting in awkward positions during long drives can start to build on that nerve pressure. If the seat doesn’t fit your body well or lacks lower back support, it becomes easy for that discomfort to creep in. The longer you’re stuck driving or sitting through traffic, the more noticeable the pain might get.
We at Align Chiropractic often see clients come in with leg or lower back pain that started or worsened after holiday travel. Our assessment is focused on understanding how the lower back, spine, and hips may be contributing.
Why Summer Driving Can Be a Trigger
Summer often brings a change in routine. Longer daylight hours and school holidays usually mean extra driving, whether that's for weekend trips or full-on holidays. Even short drives can add up when they’re happening more often than usual.
Here’s why that matters:
• Car seats often aren’t shaped to support the natural curve of the spine, which can lead to low back strain.
• When your back feels unsupported, you might shift or slump, which strains the muscles in your lower back and hips.
• Heat can add to general tiredness or body tightness, especially if you're stuck waiting in traffic with no chance to move.
On top of all that, people often skip breaks when they just want to get to a destination. Skipping those movement breaks can add to the build-up of pressure in the areas affecting the sciatic nerve. With sciatica, small triggers can add up quickly.
How Posture Plays a Role in Sciatic Discomfort
Posture might seem like a small thing, but it plays a big part in how back pain shows up, especially when you’re stuck in the car for a long stretch.
• Slouching or leaning pulls your spine into awkward positions, which puts more pressure near the base of the spine where the sciatic nerve runs.
• Hips can become tight from poor posture, pinching the nerve even more.
• Regular habits like always leaning to one side, stuffing your wallet in your back pocket, or not adjusting your seat position can make the problem worse over time.
Even a short drive with poor posture can have an effect if it's part of a daily routine. Your body remembers these patterns. Over time, they build tension and discomfort that shows up during holidays, long drives, or even just regular errands.
Some people visiting us at Align Chiropractic are surprised to learn that small adjustments in the way they sit or support their spine can change how their whole body feels after a journey.
When Support from a Chiropractor Might Help
If you’ve had this pain more than once, or noticed it improving and then returning, it may be a sign that something in your posture or movement habits is contributing to the problem. If you see one of our chiropractors for sciatica, they can check how your spine and hips are working together and see whether certain movements or positions are adding pressure to the nerve.
Chiropractic care could include:
• Looking at how you sit and move, especially after long periods of driving.
• Checking spinal movements and posture to see if anything might be affecting your lower back.
• Sharing ways that might keep pressure off the nerve while helping support more natural movement.
Sometimes, small observations lead to helpful changes. Understanding how your body is reacting can make long drives less uncomfortable and help avoid future stiffness or pain.
Enjoying Summer Without Sciatic Discomfort
Summer should be a time to enjoy the sunshine, not one spent dealing with back and leg pain after every trip. Learning what triggers your sciatica is a useful first step, especially when it's something as common as a long car ride.
Even small adjustments to driving habits or posture may make a difference. When pain shows up again and again, there might be something simple behind it. At Align Chiropractic, our care is focused on helping people understand the way posture, lower back, and daily routines work together. Noticing how your body feels after long drives 20is often the first step towards a more comfortable season.
Long drives or everyday sitting habits can bring back persistent leg or back pain, and sometimes small changes make the biggest impact over time. Speaking with our chiropractors for management of sciatica may uncover hidden factors like posture or daily routines affecting your sciatic nerve.
At Align Chiropractic, we focus on supporting you to move more comfortably, starting with a personalised approach. Reach out to us to take the next step towards lasting relief.
Understanding Migraine Patterns During Holiday Stress
It’s meant to feel like a breather, but the festive season and the new year can come with its own kind of pressure. While holidays bring time off, family gatherings, and a break from routine, they also tend to stir up more noise, more rushing around, and less time to rest properly. For those of us who experience migraines, this mix of physical and emotional stress might make symptoms show up more often than usual. We hear it each December: more tension, more changes in sleep, and more people wondering why headaches seem to flare up just when they want to feel their best.
When things start to feel tight in the neck, shoulders, or jaw, it’s often the body telling us something isn’t sitting right. That’s where a migraine chiropractor comes into the picture, not to take over your holiday health, but to help take a clearer look at how your body is coping with the season.
How Stress Affects Migraine Patterns
Stress hits more than just our mood. It tends to shift how we hold ourselves, how deeply we breathe, and how much our muscles stay switched on. In busy or emotional times, we often carry feelings in the body without even noticing. It might show up as a clenched jaw in the car, tight shoulders at the dinner table, or a stiff neck after a day of errands.
End-of-year stress can build in small, ongoing ways:
• Work pressure trying to wrap things up before the break
• Family events that are joyful but emotionally draining
• Being pulled in different directions with travel or planning
All of these can lead the body to feel tight and overloaded, which may stir up more frequent migraines. It’s not usually the stress alone but how the body responds. Muscle strain near the base of the skull or tension in the temple area can quietly increase over days. When the body holds this tension for too long without support, it becomes harder for it to relax, even when the holiday is meant to be a break.
The Physical Load of the Holiday Season
It’s easy to overlook how physical this time of year can be. Extra chores, longer drives, crowded shops, and sleep in unfamiliar beds can take a larger toll than expected. It's not just what we do, but how we move through it.
• Wrapping gifts can mean hunching over for long periods
• Lifting shopping bags or luggage can strain the lower back and neck
• Decorating may lead to overreaching or awkward twisting
• Falling asleep on the couch or in a spare bed can misalign the neck
Even small changes in habit can be enough to shift posture out of balance. A body that’s not moving the way it usually does might respond with tension-related headaches or more scattered pain. That unpredictability can be frustrating, especially when you’re just trying to enjoy the holidays.
Over the holidays, familiar routines may be replaced by new ones. Maybe you’re waking up later, carrying more, or sitting for longer meals than at other times of the year. There’s also a tendency to let posture slide while chatting with relatives or sitting on unfamiliar furniture, like folding chairs or squishy sofas at a family gathering. These little shifts can add up and put pressure on the body, especially in parts that are already sensitive from past tension.
Combined with travel, these factors become even more relevant. Whether it's a short drive or a long flight, sitting for stretches without good support often leaves your head, neck, and shoulders feeling tighter than usual. Even the way you pack a suitcase or lift out presents from the boot can spark a chain reaction that feeds back into headache patterns.
Common Areas of Discomfort Linked to Headaches
We often notice the same patterns from one end of the year to the next. When migraines get worse in December, it tends to involve a few key parts of the body.
• The upper neck, particularly near the base of the skull, can build pressure when posture slips or travel adds strain
• The jaw might feel tight from clenching during stressful conversations or busy days
• The area behind the eyes or temples may throb when tension grows slowly from stiff shoulders or awkward sleep positions
These areas are all connected more than we usually realise. When one starts to tighten, it can quickly affect the others. A migraine chiropractor looks at how these parts work together and what patterns might be forming as the season changes.
The way discomfort spreads can vary from person to person. For some, it starts at the base of the skull and radiates forward. For others, headaches might first be felt behind the eyes, especially after a day spent in bright shops or bustling environments. Muscle tension in the neck and shoulders may not be obvious at first, gradually building and then lingering as the days go by. Recognising where you feel this tightness can help you understand how the body handles strain at this time of year.
Taking Notice of Patterns Before They Build
Pain doesn’t usually arrive all at once. It comes in small signs that are easy to miss until they get louder. Paying attention to when headaches tend to appear might offer a few clues.
• After long car rides or flights, when neck posture hasn’t felt supported
• After busy social events, when crowd noise and lighting add to sensory load
• After nights of scattered or low-quality sleep
If you’ve noticed these issues in past holiday seasons, they may be showing up again for a reason. It helps to track what seems to lead into migraine symptoms rather than waiting until they fully kick in. Catching patterns early could make a big difference in how your body feels the rest of the month.
Sometimes, triggers overlap, making it hard to spot what's doing the most harm. It could be the combination of loud gatherings, rich foods, and too little downtime. Other times, it’s simply the change in sleep or the break in routine that tips things over the edge. Noting what activities or events seem to tie in with those first warning signs can make it easier to manage symptoms as the holidays go on.
A Calmer Season Starts With Listening In
When we tell ourselves headaches are just part of the holidays, we sometimes miss the body’s early warnings. There’s more going on than stress alone. The way we carry tension, shift posture, or respond to daily changes all plays a part in how migraines show up.
If your neck feels tight, your jaw sore, or your upper back heavier than usual, it’s probably time to check in. Noticing these changes and giving them space for attention can help the season feel smoother. When we stay in tune with what our body is telling us, we’re better equipped to enjoy what the holidays are meant to be.
At Align Chiropractic in South Melbourne, Dr. Martin Harvey and Dr. Kieran Whelan have expertise in treating headaches and migraines by assessing not just symptoms but also movement patterns, posture, and sources of tension in the spine and jaw. As the holiday season brings new stresses and you’re noticing changes in your migraine patterns, it’s worth exploring how neck and jaw tension might be impacting your wellbeing. At Align Chiropractic, we take a personalised approach, checking in with what your body experiences throughout these busy months. We offer support and insights for those seeking help from a migraine chiropractor. Reach out to discuss what you’ve been experiencing and how we can help.
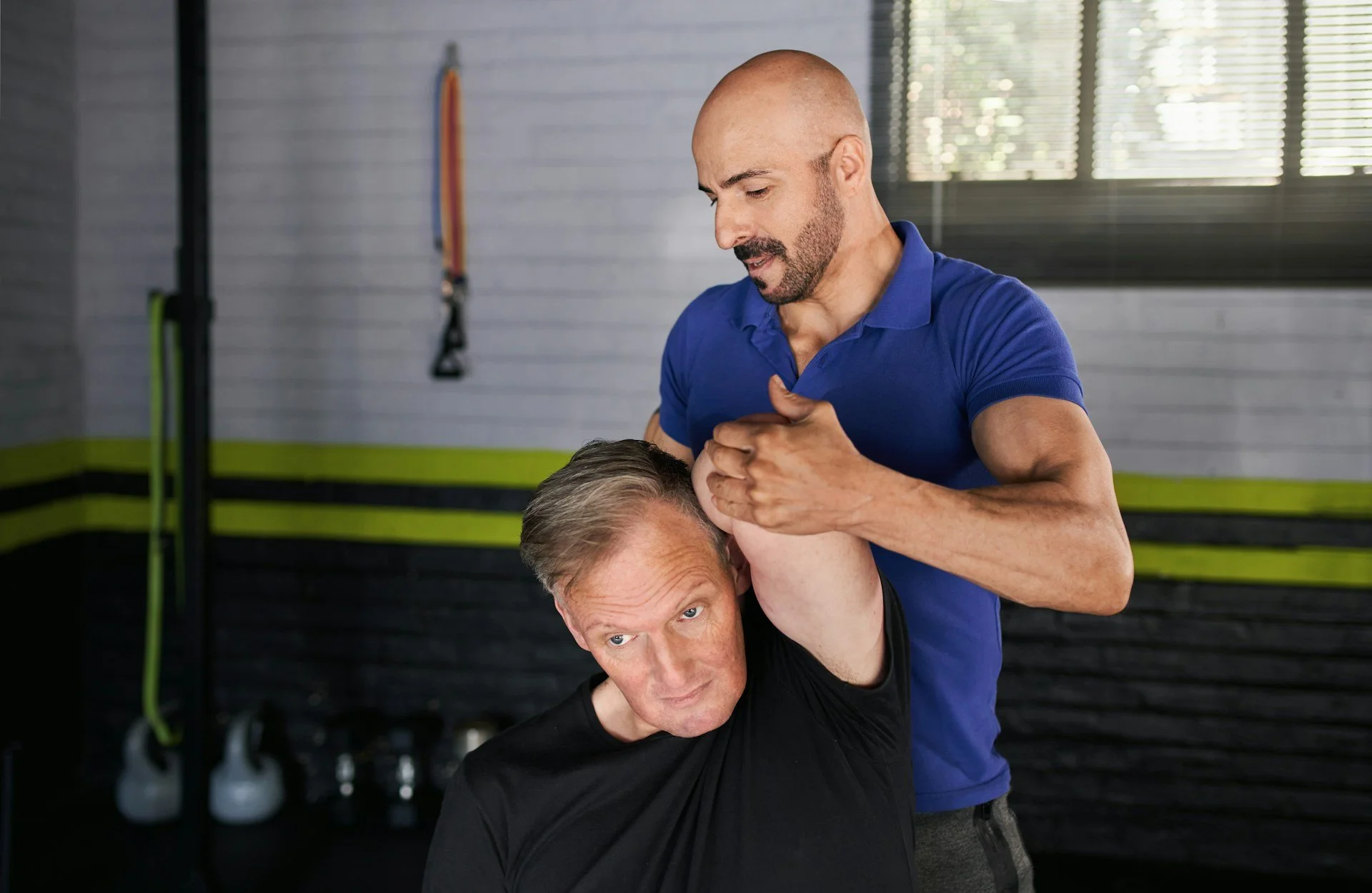
How a Chiropractor Can Support Recovery Over Summer
Summer in Melbourne brings longer days and (hopefully) warmer weather, and for many of us, that means more time outdoors.
Whether it’s casual jogs along the bay, walking or playing with the kids at the park, or simply getting back into a more active rhythm, this time of year tends to invite movement. But going from a slower pace to full-swing activity can sometimes bring a few aches along with it.
Even lightweight efforts like gardening or long walks can wake up old stiffness or leave us feeling tighter than expected. That’s where checking in with our chiropractors can help ease the transition. Paying attention to how the body’s handling the change in season matters, especially if those little twinges start showing up more often than we'd like.
Getting Back Into Activity After a Break
When we move less through winter and spring, it’s normal for the body to feel a bit sluggish come summer. Muscles haven’t had the same use, and joints might be a little less fluid. Even the most familiar activities can hit differently if we haven’t done them in a while.
We often notice the same patterns come up during this seasonal shift:
• Tight hips or hamstrings after returning to running or cycling
• Lower back stiffness from unexpected lifting or uneven surfaces
• Shoulder or neck tension after jumping back into tennis, golf, or gym workouts
It’s not just about soreness. When movement isn’t smooth, it can affect how you walk, sit, or recover at night.
A gentle review of posture and movement habits can offer insight into what’s going on under the surface. Sometimes those little misalignments or hidden strains stick around until we give them attention.
Supporting Common Areas of Discomfort
Whether you're heading out for a round of golf, dealing with post-gym tightness, or feeling the effects of sitting differently during an outdoor event, it’s often the same key areas that show wear and tear. The lower back, neck, and jaw tend to carry hidden tension, especially when we return to more regular activity.
That tension doesn’t always arrive suddenly. It might start as a dull ache or a tight spot that only shows up some days. Over time, these small imbalances can build. From repetitive swings to holding a child on one hip, the body absorbs impacts and postures in a way that often goes unnoticed, until it doesn’t.
By checking how each of these areas is responding to new or returning activity, we can better support movement and ease the kind of strain that might otherwise stick around into autumn.
How Movement Changes Through the Warmer Months
Summer brings a whole different rhythm. Swim laps in the morning, bike rides after dinner, spontaneous barefoot walks on grass, our habits change, and the body notices. Even those who keep a regular routine often tweak how or where they move during these months.
It’s common for subtle shifts in routine to have a bigger physical effect than we expect:
• Thinner-soled shoes or sandals offer less support
• Walking on sand or uneven lawns can change stride length
• Heat fatigue can influence posture during the day or how we sleep at night
Our chiropractors can help look at how joints and muscles are adjusting to these seasonal shifts. Movement might need small tweaks to feel smoother, and tuning in early can help keep activity comfortable all summer long.
At Align Chiropractic in South Melbourne, Dr. Martin Harvey and Dr. Kieran Whelan see a wide range of patients returning to sport and activity through the warmer months. We focus on checking and improving movement patterns so that tension in the back, neck, or jaw does not become a barrier to enjoying your summer activities.
Recovery Isn’t Just for Athletes
We sometimes think that recovery applies only to those in training or sport, but that’s not really the case. Summer encourages more movement for just about everyone, whether it’s playing with your kids, doing laps in the local pool, or walking more while on holidays.
Even everyday routines can start to feel off when they’ve changed dramatically:
• Lifting grocery bags differently after skipping the car park
• Trying outdoor yoga for the first time
• Sleeping in new positions due to the heat
You don’t need to be in sport to experience soreness or fatigue. When something doesn’t feel quite right, it’s okay to take note. Catching those small signs early can help you stay active without discomfort growing over time.
A Steadier Summer Starts with Comfortable Movement
Movement should feel easy, especially at a time of year when so many of us are enjoying more freedom in our schedules. Whether it’s squeezing in walks between commitments or playing backyard cricket with family, it helps when the body works with you instead of against you.
Checking in after a change in routine can be a smart way to stay ahead of any lingering tightness.
• An achy neck after road trips
• Shoulder strain from carrying things across festivals
• Back fatigue from longer afternoons out and about
We often see these patterns return each summer. By recognising them early, it’s easier to stay active, enjoy your time, and avoid letting small discomforts grow into something that limits movement later. Summer should feel light, not loaded down, and being in tune with your body makes all the difference.
At Align Chiropractic, we believe that summer is a great opportunity to tune in to what your body is telling you, especially if you notice new tension or discomfort in your back, neck, or jaw. Changes in activity can have lasting effects, so a quick assessment with a sports chiropractor can offer clarity on how you’re coping with the season. At Align Chiropractic, we focus on understanding where tension builds and what steps can help you feel your best. Reach out to book your appointment.
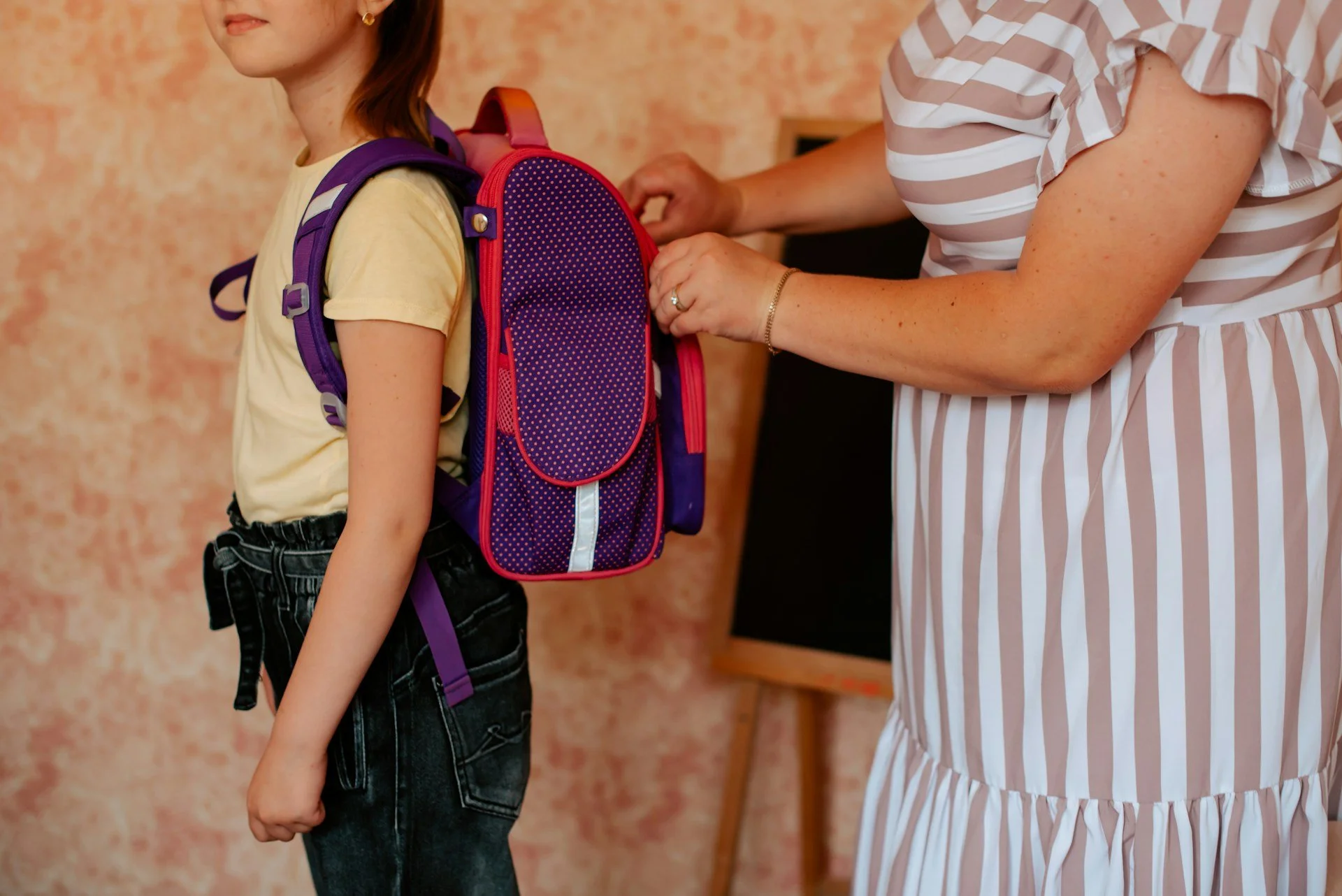
Is Your Child’s Backpack Causing Back Tension?
As the school year starts back up across Melbourne and the summer holidays come to a close, many families start preparing for the term ahead. School bags often go unnoticed in the holiday checklist, but how your child wears or packs their backpack can affect more than just what fits inside. Over time, that daily load can lead to small posture changes or tension in the back, neck, or shoulders.
These habits can build unnoticed, especially when kids are growing fast or carrying heavier items between school, sport, or sleepovers. Align’s chiropractors can assess how your child’s spine is handling day-to-day pressure.
There are also signs you can look for at home and simple changes that may help kids feel more comfortable heading into the new year.
Why Backpack Weight Matters for Kids
Most school kids carry a backpack five days a week, often loaded with books, lunch, tech, and sports gear. For a growing body, that consistent strain can take a toll. Children’s muscles and joints are still developing, so they’re more sensitive to repeated pressure and awkward posture.
• Carrying a bag that’s too heavy or lopsided can pull on the shoulders or tilt the pelvis
• If the load shifts around between classes or weeks, it can cause uneven muscle tension to build
• Kids often don’t mention pain early on, but their bodies adapt silently by leaning or walking differently
A few kilos might not sound like much, but when that weight sits in the wrong place every day, the spine notices. The lower back, neck, and shoulders often do the brunt of the work, especially if the straps aren’t adjusted well or if the bag shifts as they walk.
Common Signs Your Child May Be Feeling Tension
Children don’t always explain what’s bothering them, so small physical or behaviour changes can be even more telling. Many parents start to notice signs after school, during homework time, or getting ready in the morning.
• Their backpack stays on the floor more often than not, or they carry it on one shoulder instead of both straps on
• You might spot them rubbing their lower back, shoulders, or neck without saying anything
• Slouching while sitting, leaning to one side, or walking with slightly uneven posture
It’s not just physical. Fatigue, restlessness, or crankiness after school can sometimes relate to physical tension that’s gone unspoken. When the body’s working harder to carry strain all day, it can wear kids out in quiet ways.
How Backpack Fit and Packing Style Can Affect the Spine
How a backpack fits makes a big difference in how the load feels. Small changes in strap length, size, or what’s inside can shift how pressure flows through the spine. That’s why it helps to check how the bag sits, especially after growth spurts.
• The bag should rest snugly against the middle of the back, not sag below or bump on the hips
• Both straps should be worn, evenly tightened to keep the weight centred
• Packing heavier items closer to the body helps reduce pull on the shoulders
Bags that are too big or worn loosely lead to more shear through the spine as the load shifts while kids move. Carrying a single-strap bag or slinging the pack on one shoulder can create uneven muscle use over time, especially in the neck and mid-back. These habits may seem small in the moment but can pattern the body in ways that become uncomfortable down the road.
When to Consider a Check-In with a Chiropropractor for Pediatric Care
If you’ve noticed posture changes, new aches, or a sudden change in how your child carries their bag, it might be time for a second look. Some families check in during start-of-term transitions, periods of quick growth, or after noticing new slumping or tension.
A pediatric visit to the chiropractor looks at things like movement patterns, joint motion, and how the body is compensating. It’s not just about fixing pain but about noticing the early shifts that can sometimes lead to discomfort if left unchecked.
• Gentle guidance around posture and movement can help kids reset early habits
• Visits often involve watching how children move, stand and bend, as well as their posture overall.
• Care is light-touch and adjusted to what each child’s body feels ready for
At Align Chiropractic in South Melbourne, care is delivered by experienced chiropractors Dr. Martin Harvey and Dr. Kieran Whelan, who are familiar with working with children of all ages. The practice offers gentle, individualised approaches designed to help growing bodies move more comfortably, from young students to teenagers with increased physical demands.
Spine checks aren’t about being strict or corrective. They’re more like tune-ups, checking how the body responds to daily stress and making room for smoother, more comfortable movement.
Supporting Healthy Habits Over the Summer Break
The December break is a natural time to reset and notice details that might be harder to catch during busy school terms. The bags may be out of sight, but this is a good chance to see how your child moves without school gear weighing them down.
Summer is also full of new types of movement, from beach days and bike rides to relaxed days at home. It’s a calm window to notice posture, chat about how things feel, and gently guide better backpack habits before the next term sneaks up.
• Letting kids wear smaller bags for light day trips can help mix up loading patterns
• Watching how they carry gear on holidays can offer clues to ongoing habits
• Speaking casually about what feels good or tiring helps them learn to tune into their own comfort
No big overhauls are needed, just a chance to reset and notice how they’re carrying themselves during everyday play.
Building Confidence for the New Year
The start of the new school year is a good moment to check in on things like posture, energy, and how your child feels after carrying their school bag. Backpacks can seem simple, but they influence more than we often realise, from how a child walks to where their muscles hold tension by the end of each day.
Now that summer is settling into Melbourne, we’ve got the space to look closer at those habits. Checking how a bag fits, asking a few questions, or observing body movement can help your child feel more steady and confident when the school term starts again. Small changes now can make a difference later.
Noticing small changes in your child’s posture or signs of tension can be concerning, and sometimes it takes a professional to uncover what’s really going on. A visit with a pediatric focused chiropractor can provide valuable insight into how your child’s spine is adapting to everyday activities. At Align Chiropractic, we offer a gentle, movement-focused approach adapted to kids’ unique needs as they grow. Whether you have concerns or just want reassurance about your child’s posture, we’re here to support you and your family. Give us a call to book an appointment today.
What to Know Before Seeing a Prenatal Chiropractor in Melbourne
Pregnancy often changes how people move, rest, and carry themselves day to day. That can mean new kinds of tension in the lower back, hips, neck, or shoulders.
For those looking for gentle support through these changes, many expectant parents in bayside and South Melbourne consider in a visit to a chiropractor with a special interest in prenatal care.
A lot of mothers find that especially during the second and third trimesters, when the baby is growing fast and the body is adapting just as quickly, even small discomforts can start to add up.
It’s important that you know what to expect before walking through the door for your first visit.
Whether you’re feeling tight through the lower back or just want to check how your body is holding up as it shifts, it can help to hear how this kind of care fits into pregnancy.
Understanding Chiropractic Care During Pregnancy
Pregnancy care isn’t the same as general chiropractic.
The body’s doing a lot of work, and the approach needs to be gentle, informed, and adapted.
Someone further along in their pregnancy may lie on the table differently, and certain movements or adjustments might need to be skipped or done another way.
We often hear people mention the same kind of pressure points:
Lower back tightness, especially after long walks or sitting for too long
Pelvic strain, sometimes on one side more than the other
Subtle shifts in posture that seem to affect the neck, shoulders, or even jaw,
Tension type headaches, or ones that feel like they are coming from your neck (cervicogenic headaches).
Postural changes often begin to cause issues as your body changes.
A growing belly changes balance and can tip the pelvis forward. This may shift weight through the spine and cause extra work for the muscles keeping everything upright. That’s why care with gentle, specific, chiropractic techniques are often used during pregnancy.
The goal is always to support how the body is moving and functioning, not to push it past where it’s comfortable going.
What You Might Notice In Your Body as Things Shift
As pregnancy moves through different stages, the spine and joints tend to do a lot behind the scenes. Movement changes, sleeping positions adjust, and day-to-day tasks like walking up stairs or bending to put on shoes can feel different from one week to the next.
Some physical patterns we often hear about include:
• Neck tightness or pressure that’s new or more persistent
• Achy or sore lower backs, especially by the end of the day
• A change in walking or standing that leads to stiffness in the hips
The nervous system ties into this too, as it helps control how joints and muscles work together. When posture starts to tilt or shift, that can affect how things move in the spine and pelvis, which in turn may show up as soreness or tension across other parts of the body.
These small changes are all part of adapting, but when they build over time, they might need a bit more help to settle down.
You may also become more aware of how simple activities impact how you feel. Tasks like standing up from a chair, taking a long walk, or sleeping in a new position might feel a little different than usual.
Some people describe a general sense of tiredness in the muscles. Others might feel that their balance is a bit off, especially as their centre of gravity shifts.
All these little adjustments are normal parts of pregnancy, but it is okay to be surprised by how quickly they come and it’s normal to seek help to manage them!
What to know Before Booking Your Appointment
Before booking a visit, it’s important to know that Align, our chiropractors are experienced at seeing people from preconception, through all trimesters and even in providing post partum care.
Like you and your pregnancy, our approach is unique to you, tailored to each individual different depending on how far along in your pregnancy you are as well as your own comfort and preferences for care.
You are always in the driver’s seat..
Why Align Can Make a Difference
It’s the same every year!
Being in Melbourne during December brings its own mix of habits and routines. The weather starts getting warmer, holidays are being planned, and rest habits often shift. These little seasonal changes often lead to new posture patterns, sitting in folding chairs at parties, spending longer in the car on warm afternoons, or toggling between fans and air-conditioning during the night.
All that can affect how the body feels day to day. For those carrying extra weight from pregnancy, these shifts may feel even more noticeable!
For this reason, our care takes into into account what’s actually happening around you, so we offer a range of availability for appointments from morning into the evenings 6 days a week.
We are here to fit care around you, not the other way around!
Align Chiropractic uses gentle and personalised techniques, taking into account each patient's stage of pregnancy and unique health history. As noted on our "What to Expect" page, we offer modifications for pregnancy, and every assessment is tailored to the individual. Our experienced chiropractors in South Melbourne provide support for common pregnancy-related concerns like back, hip, and pelvic discomfort.
A Smoother Path Into the Season Ahead
Pregnancy brings all sorts of change, and sometimes it’s the small, steady things that help most. Visiting a prenatal chiropractor may offer that kind of support, quiet, ongoing check-ins with how the body is moving and feeling as it adapts.
We understand pregnancy brings unexpected changes, and having the right support can make a real difference. To help you feel prepared, we've outlined what to expect during a visit with a prenatal chiropractor and how your body may adapt, taking into account common movement patterns and what’s happening in your world at the time of your visit.
At Align Chiropractic, we're ready to answer your questions or help you book an appointment whenever you're ready.
How Posture Correction Can Help with Jaw Pressure Build-Up
Jaw tension can sneak up when life picks up pace. Whether it's long hours at the desk, late nights, or just keeping up with the rush as we enter the festive season, many people start to feel that pressure building along the sides of the face or under the ears. This tightness might feel like a dull ache, a clicking sensation, or pressure that doesn’t ease even after rest.
Often, when the focus is on the jaw, posture gets overlooked. But how we hold our body, especially through the head, neck, and shoulders, can play a big part in how the jaw feels throughout the day. Poor habits like slouching or craning the neck forward may change the way our muscles and joints are working across this whole area. Over time, that can add up to extra stress through the jaw.
Support from a posture correction chiropractor can help in looking at how alignment and daily patterns are affecting comfort levels. During stressful patches or seasons where we’re more sedentary, paying attention to posture may offer more relief than we expect.
How Posture Connects to Jaw Pressure
The link between posture and jaw tension often starts in the upper spine. When the head shifts forward, something that often happens when we’re using phones or typing on a laptop, it puts more load on the neck. That extra load needs to be carried somewhere, and it often travels through the shoulders and jaw area.
When muscles work overtime to keep us upright in a hunched position, they can become tight or fatigued. If that tension builds near the back of the jaw or around where the neck meets the skull, it may create uncomfortable pressure that lingers.
We hear signs like:
• Pressing or clenching the jaw without realising it
• Fatigue while chewing or talking for long periods
• Uneven tension between one side of the jaw and the other
When the neck and shoulders are already tight, movements like talking or eating can feel more strained than usual. The jaw, being closely connected to those areas, often ends up doing more work than it should.
Small Postural Habits That Can Build Pressure Over Time
Daily patterns shape how we carry our body. And often, the most common habits are the ones we don’t think twice about. Checking messages with the head tilted down, holding tablets close to the chest, or leaning into a screen during long meetings can all shift the spine out of its usual alignment.
These habits, repeated day after day, may slowly lead to issues like:
• Persistent forward head posture from screen time
• Long stretches in seated positions, especially without neck support
• Looking down frequently, which can tighten muscles around the jaw and neck
As we move through late spring and begin spending more time seated near fans or in cooler indoor spaces, it’s easy to remain inactive for longer. That often means more time looking at screens, reading on the lounge, or staying in one spot while working, especially during warmer afternoons. Without noticing, posture shifts to make these tasks more comfortable in the short term but less helpful in the long term.
What to Expect When Seeing a Chiropractor for Posture Support
When someone comes in with jaw pressure and neck tension, we often begin by learning more about how they hold their body during everyday tasks. The way the spine, shoulders, and head move as a unit can give helpful clues about what might be contributing to discomfort further up near the jaw.
Seeing a posture correction chiropractor is not about a quick fix. Instead, it’s about taking a closer look at how postural habits may relate to strain across the upper body.
During visits, people might experience:
• An assessment of spinal alignment and joint movement
• Gentle techniques to support better function through the neck, shoulders, and upper back
• Advice on movement habits or sitting patterns that could be adding extra tension
Rather than focus just on the jaw, this approach steps back and asks where the pressure might be starting. Often, improving movement in the upper spine helps ease tension in places that seem unrelated at first.
At Align Chiropractic in South Melbourne, experienced chiropractors Dr. Martin Harvey and Dr. Kieran Whelan offer support tailored to address underlying posture habits that may contribute to jaw, neck, and shoulder tension. Our thorough assessments are designed to uncover how lifestyle and spinal alignment may be influencing ongoing discomfort.
Supporting Better Posture During Warmer Months
As the weather turns warmer, routines tend to shift again. People might find themselves in the car more for weekend trips or working from varied locations like garden tables or outdoors under shade. These small changes in setup can affect posture in ways we might not expect.
There are a few simple things we often notice that make a difference:
• Bringing screens to eye level during work or rest can prevent forward tilting of the neck
• Taking breaks during long hours seated in cars or at a desk can reduce stiffness across the shoulders and upper spine
• Choosing seating with back support during outdoor events or holidays helps avoid slouching
This time of year also means reconnecting with social plans, more movement, and sometimes a shift in sleep patterns. All of these can nudge our posture slightly off-centre. When little adjustments at home don’t seem to ease the discomfort, having help looking at the bigger picture can be useful.
Easing Jaw Pressure Through Better Habits
It’s often surprising how connected everything feels when we take a step back. Jaw pressure rarely starts only at the jaw. The way we sit, move, and carry ourselves each day gently shapes how muscles and joints behave over time.
When we support better posture through our daily routines, we sometimes find that other areas, like the jaw, begin to ease without effort. Looking after spine alignment and movement patterns may give the body more room to relax, especially through the head, neck, and face.
Paying attention to posture isn't about being perfect. It’s about noticing which movements help us feel more comfortable and which ones might be adding tension. As we move through the warmer months, adjusting how we sit, move, and hold our head may be one way to find some relief from the pressure we didn’t realise we were holding on to.
At Align Chiropractic, we know how much your posture habits can affect the comfort of your jaw, neck, and shoulders each day. When ongoing tension or discomfort is getting in the way and at-home adjustments aren’t making enough difference, it could be time to look deeper into the underlying cause. Working with a posture correction chiropractor can help you understand what your body is signalling and support you in moving with greater ease. Let’s talk about your needs and discover what could help you feel your best.
Chiropractic Adjustment or Rest: What's Better for Sciatica?
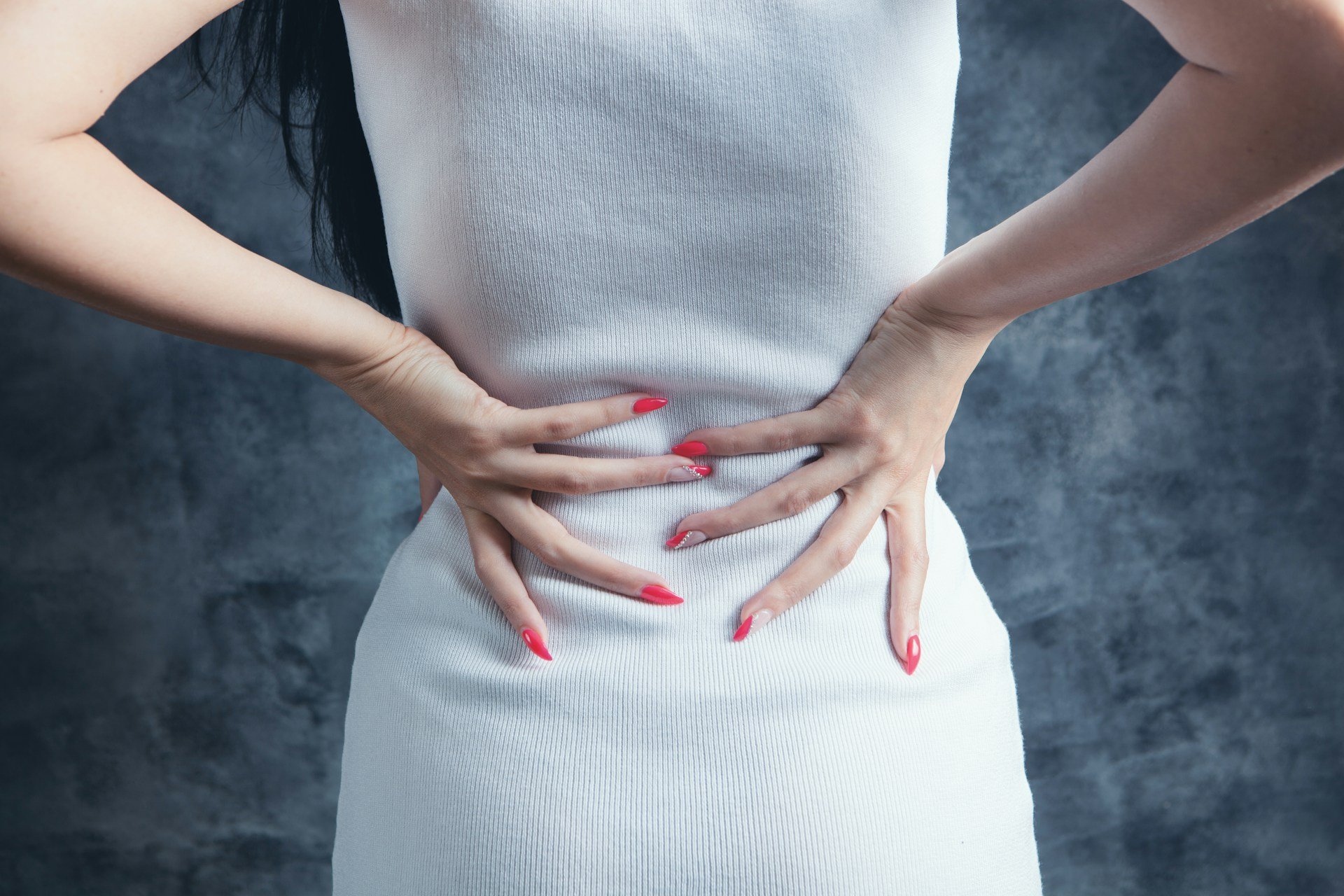
Sciatica can stop you in your tracks. That sharp, shooting pain that moves from the lower back down through the hips and legs can make the simplest movements feel hard.
When you're in the middle of a flare-up, it's common to wonder what will help most.
Is rest enough, or would something like a chiropractic adjustment give your body the support it needs?
With warmer months ahead across much of Australia, many people become more active, making it a good time to talk about how rest, movement, and spinal care each play a role when sciatica shows up.
Understanding Sciatica and Why It Hurts
Sciatica refers to irritation of the sciatic nerve, the thickest nerve in the body. It starts in the lower back, travels through the hips and buttocks, and runs down each leg. When this nerve gets pinched or inflamed, pain can appear suddenly or build up over time.
• People often describe sciatica as a sharp, burning, or tingling feeling, usually on one side of the body
• Long hours sitting, suddenly bending, lifting awkwardly, or staying inactive too long can all put added pressure on the lower spine
• Sometimes, the nerve gets compressed by spinal joints or tight muscles deep in the pelvis
Pain isn’t always constant. For some, it comes and goes based on how they sit or move. Others may feel it most when standing up or sleeping. Understanding what actions might trigger it is often the first step toward feeling better.
Does Rest Help or Make Things Worse?
When sciatica hits hard, it's normal to want to lie still. In the early stages of pain, short periods of rest can give the body a breather. Especially during those first hours or days of sharper discomfort, being gentle with movement may help reduce stress.
• Resting in a supportive position, like lying on your back with pillows under your knees, may feel more comfortable
• Avoid curling up or sinking too far into a lounge, which can push your pelvis into a shape that strains the lower back
• Short breaks throughout the day are often better than staying in one place for hours at a time
Having said this, too much time lying down can work against you. Muscles tighten when held too long in one position, blood flow slows, and joints can stiffen.
The key for many people is to balance short, helpful rest with small movements that keep the body from tightening up more.
How Movement Supports Healing
Even small movements can play a helpful role when you're working through sciatica. Unless the pain is too sharp to walk, gentle activity tends to help the body recover more steadily than lying still all day.
• Short walks, even around the house, can support nerve and blood flow
• Light stretching or gentle core support movements (done in line with what feels comfortable) may take pressure off the lower spine
• Keeping good posture when sitting or standing helps reduce extra strain on the irritated nerve
Moving more doesn't mean pushing through pain. It means listening to what your body will allow and avoiding heavy or jerky motions.
Can Chiropractic help sciatic pain?
When pain feels stuck, or movement doesn’t change much, it's natural to want another path.
A chiropractic adjustment is a hands-on way to improve how joints in the spine move. It involves gentle and specific movements applied to joints that may be restricted or not moving well, especially in the lower back or pelvis.
• By improving spinal motion, a chiropractic adjustment may help take pressure off areas irritating the sciatic nerve
• Smoother joint movement can lead to better muscle balance, which often helps the body move more freely
• For some, this type of care feels helpful when their regular habits haven’t made much difference
At Align Chiropractic, Dr. Martin Harvey and Dr. Kieran Whelan use our extensive experience to focus on relieving pressure in the spine, pelvis, and related muscles.
The care we provide is specific and individualised, with thorough assessments to identify the underlying factors contributing to pain. This patient-centred approach is designed to help people in South Melbourne and surrounding areas move more freely and recover from sciatica flare-ups with confidence.
It's not about cracking or forcing the spine. It's about looking at how things are moving and helping the body work in a more balanced way. Anything that reduces the everyday pressure on the lower nerves may shift how sciatica feels.
Finding Your Best Path Forward
Every body is different. What helps one person’s sciatica feel better might not be the same for someone else, which is why it makes sense to pay close attention. Being too still or too active can both stir things up. Figuring out that middle ground takes time, and some trial and error.
• Gentle movement, well-timed rest, and support from trusted health providers each play a part
• Summer usually means more plans, more travel, and more time outside, which many find puts new stresses on the spine
• Catching early signs of back or leg discomfort can help avoid longer flare-ups
When sciatica strikes, the goal isn’t just to get through the pain but to understand what your body needs to move and feel better long-term. Watching those patterns and adjusting your habits often makes a bigger difference than doing just one thing.
At Align Chiropractic, we understand how disruptive sciatica can be, especially during busy times of the year. Not sure whether movement, rest, or extra support is right for you? Discover how a well-timed chiropractic adjustment can support your spine and help relieve tension in your lower back and pelvis. We’re here to help you find what works for you. For guidance tailored to your needs, contact us to book a visit.
What Makes Neck Pain Feel Worse in Late Spring
Introduction
As the days grow warmer and Melbourne shifts into late spring, many of us start to feel the stirrings of summer. Longer daylight hours, changing routines, and bursts of outdoor activity can be uplifting after the winter stretch. But for some, this shift also brings a familiar ache in the neck and shoulders that seems to come out of nowhere.
We often hear clients mention that their neck pain feels sharper or more persistent this time of year. These are not isolated complaints. A chiropractor for neck pain will often notice seasonal patterns in discomfort. The way our environment changes in late spring can have more of an impact on our muscles and posture than we realise. Small shifts in daily habits can sneak up on your body and may lead to increased strain in your neck.
How Seasonal Changes Can Affect Your Neck
Late spring doesn’t just bring warmer air, it invites us outdoors and often asks more from our bodies. As we transition away from cooler, slower months, some muscle reactions can take us by surprise.
• Sudden changes in temperature, especially in the mornings and evenings, can cause neck muscles to tighten or stiffen
• Extra outdoor activity, such as weekend sports or walks, can involve new or repetitive movements in the upper back and neck
• Air conditioning becomes more common, especially indoors and in cars. Cold air blowing directly across the shoulders and neck can lead to tension building up without us noticing
Even something as simple as shifting from layering up in winter clothing to lighter garments can affect how our neck and shoulders respond throughout the day. The body adapts quickly in some ways and slowly in others. If our lifestyle speeds up but our spine or muscles haven’t caught up, it’s easy to understand why pain gets worse, rather than better.
Springtime Posture Triggers in Everyday Life
As late spring rolls in, our habits and surroundings change, sometimes in unexpected ways. And these changes can directly influence how we carry ourselves.
• Many of us move our home workspace to lighter spots like verandas, patios, or cafés. These more casual setups often lack proper support, which can put the neck in awkward positions
• Gardening becomes a common springtime activity. Weeding, planting, and digging often involve hunching forward, twisting, or looking down for long periods
• With sports restarting or events becoming more frequent, we're often lifting bags, supplies, or children without thinking much about it. All of these actions can place extra load on the neck and upper back
Posture isn't just about standing up straight. It's about how everyday movements add up over time. If we're consistently craning, slouching, or rotating without balance, the body eventually lets us know.
Stress Patterns and Sleep Shifts Around Spring
It’s not just our physical movements that affect the neck. Our thinking, sleeping, and daily rhythms play big roles too. Spring can be uplifting, but it’s also busy.
• Social calendars often fill up. With more outings, tasks, or travel plans, stress levels can rise, and that tension usually lands right between the shoulders
• Allergies tend to flare in spring. Along with discomfort, congestion may change how we sleep or breathe, leading some people to clench their jaw or hold their neck stiff
• Longer days and earlier sunrises can change sleep timing. Less restful sleep means muscles don’t recover properly overnight, leaving the neck more prone to discomfort the next day
Stress doesn’t always look like worry or anxiety. Some people feel it as extra tightness in the top of the shoulders or an ache that shows up when trying to relax. These clues are often overlooked but can be very telling.
How a Chiropractor for Neck Pain May Offer Support
If spring shifts are bringing more than just flowers and sunshine, it might be time to check in with how your body’s adapting. We often see how these seasonal shifts show up in the spine and surrounding muscles.
• By looking at posture, movement habits, and muscle function, we can help figure out what's contributing to increased neck pain
• Chiropractic adjustments may offer relief by addressing tension, improving joint movement, and reducing any areas that feel extra tight or restricted
• The most important part of support is often planning ahead, especially if neck tension seems to come back each year around the same time
All care at Align Chiropractic is delivered by highly experienced practitioners, Dr. Martin Harvey and Dr. Kieran Whelan, have decades of expertise in addressing neck pain, headaches, and posture-related issues. We take a personalised approach, assessing both spinal alignment and how individual lifestyle factors in South Melbourne can influence recurring neck discomfort.
Rather than chasing symptoms, it may be helpful to understand patterns. Spring routines don’t have to be painful. Sometimes it's just about giving the body a chance to reset and move in healthier ways.
Late Spring, Lasting Relief
Late spring brings a lot of change, most of it welcome. But if you’ve been noticing your neck feeling more achy than usual, there could be a reason behind it. Whether it's small shifts in daily posture, disrupted sleep, or more time running around, the neck often picks up the slack.
Take this time of year as a reminder to check in on your daily posture and movement habits. If tension or discomfort persists, working with experienced chiropractors in South Melbourne could help you move comfortably through the season and beyond.
As spring brings changes in temperature, activity, and sleep, subtle tension in your neck and shoulders can build up before you even notice. We help people uncover these patterns and support ongoing wellbeing with gentle, personalised care. When you need a chiropractor for neck pain who understands the impact of seasonal shifts, Align Chiropractic is here to help you feel your best. Reach out today to book a time that works for you.
Why Neck Pain Can Hit Harder in Late Spring
As the days grow warmer and Melbourne shifts into late spring, many of us start to feel the stirrings of summer. Longer daylight hours, changing routines, and bursts of outdoor activity can be uplifting after the winter stretch. But for some, this shift also brings a familiar ache in the neck and shoulders that seems to come out of nowhere.
We often hear clients mention that their neck pain feels sharper or more persistent this time of year. These are not isolated complaints. A chiropractor for neck pain will often notice seasonal patterns in discomfort. The way our environment changes in late spring can have more of an impact on our muscles and posture than we realise. Small shifts in daily habits can sneak up on your body and may lead to increased strain in your neck.
How Seasonal Changes Can Affect Your Neck
Late spring doesn’t just bring warmer air, it invites us outdoors and often asks more from our bodies. As we transition away from cooler, slower months, some muscle reactions can take us by surprise.
• Sudden changes in temperature, especially in the mornings and evenings, can cause neck muscles to tighten or stiffen
• Extra outdoor activity, such as weekend sports or walks, can involve new or repetitive movements in the upper back and neck
• Air conditioning becomes more common, especially indoors and in cars. Cold air blowing directly across the shoulders and neck can lead to tension building up without us noticing
Even something as simple as shifting from layering up in winter clothing to lighter garments can affect how our neck and shoulders respond throughout the day. The body adapts quickly in some ways and slowly in others. If our lifestyle speeds up but our spine or muscles haven’t caught up, it’s easy to understand why pain gets worse, rather than better.
Springtime Posture Triggers in Everyday Life
As late spring rolls in, our habits and surroundings change, sometimes in unexpected ways. And these changes can directly influence how we carry ourselves.
• Many of us move our home workspace to lighter spots like verandas, patios, or cafés. These more casual setups often lack proper support, which can put the neck in awkward positions
• Gardening becomes a common springtime activity. Weeding, planting, and digging often involve hunching forward, twisting, or looking down for long periods
• With sports restarting or events becoming more frequent, we're often lifting bags, supplies, or children without thinking much about it. All of these actions can place extra load on the neck and upper back
Posture isn't just about standing up straight. It's about how everyday movements add up over time. If we're consistently craning, slouching, or rotating without balance, the body eventually lets us know.
Stress Patterns and Sleep Shifts Around Spring
It’s not just our physical movements that affect the neck. Our thinking, sleeping, and daily rhythms play big roles too. Spring can be uplifting, but it’s also busy.
• Social calendars often fill up. With more outings, tasks, or travel plans, stress levels can rise, and that tension usually lands right between the shoulders
• Allergies tend to flare in spring. Along with discomfort, congestion may change how we sleep or breathe, leading some people to clench their jaw or hold their neck stiff
• Longer days and earlier sunrises can change sleep timing. Less restful sleep means muscles don’t recover properly overnight, leaving the neck more prone to discomfort the next day
Stress doesn’t always look like worry or anxiety. Some people feel it as extra tightness in the top of the shoulders or an ache that shows up when trying to relax. These clues are often overlooked but can be very telling.
How a Chiropractor for Neck Pain May Offer Support
If spring shifts are bringing more than just flowers and sunshine, it might be time to check in with how your body’s adapting. We often see how these seasonal shifts show up in the spine and surrounding muscles.
• By looking at posture, movement habits, and muscle function, we can help figure out what's contributing to increased neck pain
• Chiropractic adjustments may offer relief by addressing tension, improving joint movement, and reducing any areas that feel extra tight or restricted
• The most important part of support is often planning ahead, especially if neck tension seems to come back each year around the same time
All care at Align Chiropractic is delivered by highly experienced practitioners, Dr. Martin Harvey and Dr. Kieran Whelan, have decades of expertise in addressing neck pain, headaches, and posture-related issues. We take a personalised approach, assessing both spinal alignment and how individual lifestyle factors in South Melbourne can influence recurring neck discomfort.
Rather than chasing symptoms, it may be helpful to understand patterns. Spring routines don’t have to be painful. Sometimes it's just about giving the body a chance to reset and move in healthier ways.
Late Spring, Lasting Relief
Late spring brings a lot of change, most of it welcome. But if you’ve been noticing your neck feeling more achy than usual, there could be a reason behind it. Whether it's small shifts in daily posture, disrupted sleep, or more time running around, the neck often picks up the slack.
Take this time of year as a reminder to check in on your daily posture and movement habits. If tension or discomfort persists, working with experienced chiropractors in South Melbourne could help you move comfortably through the season and beyond.
As spring brings changes in temperature, activity, and sleep, subtle tension in your neck and shoulders can build up before you even notice. We help people uncover these patterns and support ongoing wellbeing with gentle, personalised care. When you need a chiropractor for neck pain who understands the impact of seasonal shifts, Align Chiropractic is here to help you feel your best. Reach out today to book a time that works for you.
How Neck Issues Might Be Linked to Jaw Discomfort
Small posture habits can lead to discomfort. Learn how the jaw pain in the neck connection could be affecting your daily comfort and movement.
When people think about jaw pain, they usually do not think of their neck, but for many, the two can be more connected than you might expect. The link can be easy to miss, especially if the pain has crept in over time. You might feel it when you yawn, chew, or sit at your desk for too long. The jaw pain neck connection can be tricky. It is not always sharp or sudden. It might start off as a bit of tension or discomfort that slowly builds and spreads.
Paying closer attention to the way your neck lines up with the rest of your body could make a difference. Let us look at how the jaw and neck work together, and why posture might play a bigger role than you realise.
How the Jaw and Neck Are Physically Connected
The jaw and neck operate as a team. They share a group of muscles and joints that help us move our heads, chew food, speak, and maintain a steady posture. So when one area feels off, the other often tries to pick up the slack.
The muscles that move the jaw, like the ones used for chewing, are closely tied to muscles that support the neck and shoulders.
When you have poor posture, especially a forward head position, it can place more strain on these areas. That strain can pull on muscles around the jaw, creating pressure or tightness.
If the neck is restricted or out of balance, it might also change the way the jaw opens and closes. That can lead to uneven movement or added stress to one side.
So even if the pain feels like it is only in the jaw, part of the trouble could be coming from somewhere else.
Common Signs Your Jaw Pain Might Be Linked to Your Neck
It can be tricky to figure out where pain is really coming from, especially when symptoms overlap.
There are a few signs that might point to a connection between the jaw and neck.
You notice pain that travels from the neck to the jaw, or the other way around.
Your neck feels stiff, or it is hard to turn your head comfortably.
Holding your head up for long stretches (like working at a desk or scrolling on your phone) brings on more discomfort.
You feel a tight, dull ache in your temples, around your ears, or near your jaw joints when you clench.
There is a sense of pressure on the teeth or face, but not always any dental cause.
If these sound familiar, the discomfort might not be just about the jaw. Our bodies often work in
patterns, and noticing those patterns can help make sense of what you are feeling.
Everyday Habits That Might Be Affecting Your Neck Posture
Sometimes it is not just an injury or strain that causes pain. Habits throughout the day may
slowly nudge our posture out of alignment, putting stress on areas like the neck and jaw without us even realising it.
Looking down at phones or laptops for long periods can train your neck into a forward-leaning position.
Sitting with rounded shoulders or poor back support can shift your entire head forward, adding weight and pulling on your neck.
Sleeping on your stomach or with the wrong kind of pillow can push your neck into awkward angles for hours at a time.
One or two of these habits here and there will not usually cause big problems. But day after day, they can add up and put pressure on the muscles you rely on most.
What Support Might Look Like for Jaw and Neck Issues
When these kinds of problems show up, assessing posture and how the body moves can be a helpful first step. Every person is different, so it helps to focus on your own patterns and needs.
As chiropractors we start with a check of how your neck, shoulders, and jaw move and feel.
You might be shown small posture changes or gentle movements that aim to ease tension.
Instead of a quick fix, steady changes over time, like better desk habits or changes in sleeping positions, can bring more daily comfort.
At Align Chiropractic in South Melbourne, Dr Martin Harvey and Dr Kieran Whelan have over four decades of combined experience working with patients dealing with neck pain, jaw
discomfort, headaches, and posture-related issues. Their approach involves careful assessment and understanding of how these areas interact, with patients from Albert Park, Port Melbourne, St Kilda, and nearby suburbs seeking help for similar conditions.
Support often looks different from one person to the next. By learning what may be affecting you and making small shifts, your day-to-day comfort might improve bit by bit.
A Healthier, More Aligned You
We do not always think about how things like posture or screen time might affect other parts of the body. But the connection between the jaw and the neck is one that can make a real difference in how we feel from morning to night. Noticing patterns, listening to your body, and making small changes can sometimes help ease pain or tension. With a bit of awareness and the right kind of support, we believe many people can find more ease in how they sit, move, and rest.
Wondering why jaw pain seems to stick around with neck tension or stiffness? The way our muscles and joints interact means discomfort can often move or build across different areas. We often notice this in the jaw pain in the neck connection, which can sometimes go unnoticed. At Align Chiropractic, we focus on noticing these patterns to help guide the right kind of support. If some of these signs are sounding familiar, get in touch so we can chat about what might be happening and how we may help.
The Aligned Life Podcast: Episode 3
How Daylight Savings Can Wreck Your Week
Ever notice how one lost hour can throw everything off? You feel fine, but you’re not!
Focus slips. Energy crashes. You reach for more coffee and think it’s just a busy week - when it’s actually sleep debt.
This week, Martin and Kieran unpack what daylight savings really teaches us about sleep.
It’s not just about feeling tired, it’s about how even mild sleep loss messes with your brain, hormones, and mood.
They break down why your body treats sleep like oxygen, it’s not a luxury, and how to reset your rhythm when life (or the clock) knocks it out of sync.
🎧 Listen now on Apple Podcasts, Spotify or wherever else you listen to your new favourite podcasts!
Heres to better health and more restful days,
Dr Martin Harvey & Dr Kieran Whelan
P.S. Got a question for the show? Reply with “Podcast Q:” in the subject and we’ll queue it up. If this episode helps, hit reply and tell us what landed—or share it with a friend who needs a reset.
The aligned life podcast: Episode 2
Why meditation fails when you’re most stressed (and what actually helps)
This, the newest episode of the Aligned Life podcast is a simple “bottom-up” reset to calm your body first—so your mind can follow.
Hi there!
Ever been told to “just meditate”… when your brain is doing cartwheels?
Same. When stress is high, “top-down” tools (think: meditation, reframing, CBT) can feel impossible.
In today’s new episode of The Aligned Life, we flip the script:
The Stress Reset: Calm Your Body Before Your Mind
Martin and Kieran break down a bottom-up approach with simple body-led tactics that signal safety to your nervous system so your mind finally has space to exhale.
In 25 minutes, you’ll learn:
Why top-down tools fail when you’re overloaded (it’s not your fault - your frontal cortex is offline)!
The walk + breath combo we use to lower physiological arousal in minutes.
A 60-second posture reset that breaks the “shoulders-up, jaw-tight” loop.
When HIIT exercise can help and when it secretly fuels burnout.
How chiropractic adjustments may support nervous system adaptability (hello HRV!).
PLUS, as usual, Martin and Kieran discuss their local picks of the week, Halcyon Days and Italian Artisans in Albert Park because life’s more than stress!
Coming up: don’t forget The Stress Reset Challenge
We’re launching a 5-day, 5–20 min/day challenge to help you test what works in real life—walking, breathwork, micro-breaks, posture, and more. It’s open to everyone, not just patients. Details in the next episode.
To more calm days,
Dr Martin Harvey & Dr Kieran Whelan
P.S. Got a question for the show? Reply with “Podcast Q:” in the subject and we’ll queue it up. If this episode helps, hit reply and tell us what landed—or share it with a friend who needs a reset.
🎧 Listen now on Apple Podcasts, Spotify or wherever else you listen to your new favorite podcasts!
The aligned life podcast: Episode one
We’re thrilled to announce the very first episode of The Aligned Life Podcast, hosted by Dr. Martin Harvey and Dr. Kieran Whelan, chiropractors at Align Chiropractic in South Melbourne.
This podcast is all about helping you live a healthier, happier, more active life — with simple, natural, science-backed ways to boost your energy, improve your posture, sleep better, manage stress, and feel your best.
Episode 1: Stuck on Stress -
In this episode, Martin and Kieran dive into one of the biggest health challenges of our time: stress. They unpack why stress levels are on the rise, how it impacts your body and mind, and most importantly, what you can do about it.
Here’s what you’ll learn:
Why nearly half of Australians report high stress levels — and why it’s worse in cities.
How stress shows up physically (neck pain, headaches, posture changes, jaw clenching) and mentally (brain fog, anxiety, low mood).
The difference between “good stress” that helps us grow and “bad stress” that wears us down.
Top-down vs bottom-up strategies for managing stress — from meditation and journaling to chiropractic care, posture, exercise, breath-work, and even time in nature.
Sneak peek of the upcoming 5-Day Stress Reset Challenge, designed to help you move from theory to practice with easy, bite-sized tools you can try at home.
Takeaway: Stress isn’t just “in your head”, it’s in your body too but with the right strategies, you can break the cycle and reclaim calm, focus, and energy.
Tune in now to the first episode of The Aligned Life Podcast and start your journey to a more aligned, resilient life.
Give it a listen: on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts.
Dive into the Chilly World of Cold Exposure: Unlocking the Benefits of Cold Water Immersion
The photo above is of Martin taking his very first ice bath. It was in September last year and he has been embracing the cold ever since. Martin started because he had heard that regular cold exposure was good for your health (more on that below) but have kept going because I feel great after every ice bath and cold shower.
Have you ever considered taking the plunge into cold water or braving a refreshing cold shower? You might think it sounds crazy, but let me tell you, the rewards are worth it! Cold exposure has some incredible benefits for your body and mind. So, let's chat about why embracing the cold can be a game-changer in your quest for overall well-being.
First off, when you expose yourself to the cold, something magical happens. Your brain and body release adrenaline and noradrenaline, which amp up your alertness and energy levels. It's like a natural boost that makes you feel alive and focused. As well, those effects last even after you've dried off!
So, if you've been feeling a little sluggish or struggling to concentrate, a cold shower or a dip in icy water might just be the jolt you need to kickstart your day.
Cold exposure isn't just about waking you up—it's also about building resilience and grit.
When you willingly subject yourself to the discomfort of the cold, you're training your mind to handle stress better. It's like a mental boot camp. By challenging yourself and pushing through the initial shock, you strengthen your ability to stay calm and composed when faced with real-life challenges. It's a skill that extends far beyond the cold showers. It's a superpower that helps you tackle whatever life throws your way.
Now, let's talk about mood enhancement. Who doesn't want a little extra happiness in their life? Cold exposure has got your back. When you expose yourself to the cold, your body releases dopamine—a neurotransmitter responsible for pleasure and motivation. And let me tell you, dopamine is a game-changer. It lifts your mood, boosts your energy, and enhances your focus and productivity. So, the next time you're feeling a bit down or lacking motivation, why not take a dip in cold water and let the dopamine work its magic?
Oh, and here's an interesting tidbit: cold exposure can actually rev up your metabolism. When your body is exposed to cold temperatures, it has to work harder to keep you warm. That extra effort translates into burning more calories. But the real kicker is the transformation of white fat into beige or brown fat. Unlike white fat, these metabolically active fats keep your body humming, giving you that extra edge in your weight management journey.
So, it's time to embrace the cold and reap the rewards. Start with shorter cold showers and work your way up to longer durations or even try an invigorating ice bath. Listen to your body, take it one step at a time, and enjoy the benefits of increased energy, resilience, enhanced mood, and a revved-up metabolism. Trust me, your body and mind will thank you for taking the plunge into the chilly world of cold exposure. It's time to make waves and dive into a whole new level of well-being.
If you’re keen to take the plunge we have arranged an ice bath event for Align Clients at The Recovery Lab, Windsor. It’s on Saturday June 17th from 7am- 8am. The ice baths will be at around 8 degrees and we suggest that you aim to do around 3 minutes. Martin will do a brief talk about strategies you can use to do the ice bath (and enjoy the experience) and then you will get a chance to take the plunge! Tickets are available here.
Are you tired of headaches holding you back?
Tired of being held back by headaches?
Spinal Health Week 2023 was 22-28 May and it is here to help!
It's a national campaign by the Australian Chiropractors Association (ACA) that focuses on improving spinal health for all Australians.
This year, Spinal Health Week highlighted the impact of headaches and providing solutions to relieve your pain. Did you know that over 7 million Australians suffer from tension headaches and more than 4.9 million have chronic migraines?
The cost to the country is a whopping $35.7 billion every year. But the real cost is immeasurable—headaches affect 46% of Australians daily, causing pain, disrupting work and study, and stealing quality time with loved ones.
Headaches come in different types and have various triggers. Some are mild inconveniences, while others can be severe and chronic, severely impacting daily life. Research shows that spinal health, especially in the neck, is closely connected to headaches. That's why it's important for headache sufferers to have their spines checked and consider drug-free chiropractic care. Along with some simple lifestyle changes, this approach can go a long way in reducing pain, preventing headaches, and helping you regain control of your life.
Studies have shown that chiropractic care is effective for the most common headaches: tension headaches, cervicogenic headaches (neck-related), and migraines. In fact, chiropractic adjustments have been shown to reduce migraines in 72% of people surveyed, decreasing their duration and severity. While pain medications may provide temporary relief, they only treat the symptoms and not the underlying cause. Lifestyle factors, like diet and sedentary habits, can also contribute to headaches. Chiropractors can identify these factors and help you make changes to manage or even avoid headaches, improving your overall well-being.
At Align Chiropractic, our team of ACA-accredited chiropractors are trained to find the causes of headaches and provide safe, drug-free care for people of all ages. If you or someone you know is among the 11.9 million Australians suffering from headaches or migraines, it's time to take action.
Contact us today at 03 9696 1057 or book online at alignchiropractic.com.au to schedule an appointment and regain control of your life.
For more information on the importance of spinal health and how it affects you and your family, visit spinalhealthweek.org.au. Join the #SpinalHealthWeek movement and say goodbye to headaches holding you back!
#SpinalHealthWeek #ConsultAChiro #Headache #HeadacheConsultAChiro #southmelbourne #albertpark
What are the benefits of NOT eating?
Intermittent fasting has been gaining popularity in recent years as a way to improve health and lose weight. But what exactly is intermittent fasting and why should you consider incorporating it into your lifestyle?
Through February, the team at Align Chiropractic will be doing a 28-day "Fast Start" Intermittent Fasting Program based on the approach from "Fast, Feast, Repeat," and we would love for you to join us. It will be a great way to give your health a kickstart and maybe even lose weight.
We will be hosting a 1-hour "Intermittent Fasting" info session.
On Zoom at 12:30 on Thursday, January 25th. It’s free and you can register here.
The "Feb Fast" challenge will kick off on February 1st.
Intermittent fasting is a pattern of eating that involves regular periods of fasting, followed by periods of eating. There are several different methods of intermittent fasting, including the 16/8 method, the 5:2 diet, and alternate day fasting.
One of the main benefits of intermittent fasting is weight loss. When you fast, your body is forced to use stored fat as energy, which can lead to weight loss. In addition, intermittent fasting may help to regulate appetite and reduce cravings for unhealthy foods. A review of intermittent fasting studies found that it was an effective way to lose weight and improve metabolic health markers.
But weight loss is just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to the benefits of intermittent fasting. Studies have shown that intermittent fasting can have a number of other health benefits, including:
Improved insulin sensitivity: A study in people with type 2 diabetes found that intermittent fasting led to improvements in insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
Decreased inflammation: A review of studies found that intermittent fasting may reduce inflammation in the body.
Increased lifespan: Some animal studies have suggested that intermittent fasting may increase lifespan by promoting cellular repair and reducing oxidative stress.
Improved mental clarity: Many people report increased mental clarity and focus while fasting, which may be due to the increased production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).
Intermittent fasting is not for everyone. However, for those who are able to incorporate it into their lifestyle, the benefits of intermittent fasting can be numerous and significant. So why not join the team at Align Chiropractic and give it a try? You might just find that it works for you.
Research Exposure Therapy 1. A Case study on mood.
OK so this one might be a little different.
I thought that this year I would do something I have never done here before and actually use this blog space more like an ongoing blog.
To remain registered as a chiropractor, Martin and I have to meet certain standards, and part of those standards is ongoing education.
Often Martin and I will find ourselves reading research papers or hear about new research that changes how we practice, or has us excited about how we practice that has significant impact for the clients that we are lucky enough to see.
As always, we meet weekly, discuss the information and then try to implement it into our practice as we constantly strive to improve our care, but there might be a lot of you who are actually keen to learn along with us.
Which leads me to this post, I am not sure what form this will take eventually, but what I was wanting to do with them is not to just present the information like a summary of the research, but I would love for people to see what information is out there and then understand why it is significant to us at Align and you as a client.
I’m not intending to explain the methods etc, though I will always provide the citation for you. My goal is to outline what is some interesting research I have come across, and hopefully encourage people to understand more, perhaps it will be relevant to them or to a loved one, but we would like to encourage you to discuss it with Martin or myself if it does pique your interest.
So without further preamble. The research:
Hughes F. (2020) “Reduction of cortisol levels and perceived anxiety in a patient undergoing Chiropracticmanagement for neck pain and headache: a caseReport and review of the literature,” Journal of Contemporary Chiropractic, https://journal.parker.edu/index.php/jcc/article/view/95
Now to start with, a disclaimer, this is a case study only and as such is a starting point for further research, NOT a definitive research answer. Individual results of care may vary. If you have any questions about research design and why some are more highly valued compared to others, please ask Martin or myself.
In this case study, a chiropractor was managing the care of a lady suffering from neck pain and headaches.
As part of the care provided, the chiropractor had the client complete surveys regarding her mental state as well as for pain etc. and the client also had her cortisol (or stress chemical) levels measured at the outset and as reassessment points in her care.
What was discovered was that through ongoing chiropractic care including adjustment and home advice, not only did her neck pain and headaches improve, but the client’s cortisol levels decreased significantly as well as the client herself feeling less anxious in her day to day life.
This particularly stood out to us as anxiety was NOT what the client was intending to have managed by the chiropractor, nor was it the focus of the chiropractor’s care plan for the client, yet areas outside the initial complaint significantly improved, creating a better quality of life for the client.
This was significant to me as it certainly reflects what we often see in practice with out clients. Often we will have clients state how much more relaxed they feel after an adjustment, or that they can breathe easier, or a “weight has been lifted from their shoulders”.
This has been particularly common throughout the last 2 years as we have had…lets say more stress than is normal in our day to day lives because of the pandemic.
The main reason I was inspired to write something here though is because often when we are busy or when people have significant injuries etc that we are managing, as a practitioner it is easy for us to focus on just the issue clients might present with and in doing so, we might be missing significant contributing elements.
For clients this might be more important, as imagine if there was another issue you were putting up with and even though myself or Martin were in a position to help, we are not aware that we could be working with you to get on top of other issues at the same time.
At Align we use specific surveys to get a snap shot of where a client will be in regard to mood, energy, concentration and attempt to track these over time, but going forward, I want to make sure I am encouraging our clients to make sure they are getting the most out of their care.
If there is something else bothering you or you aren’t sure we could help with, then we would love for you to feel free to ask us. Hopefully we are in a position to help you, but even if we are not, I am confident that we will be able to find the right person who CAN help you with whatever issue you might have.
The advantage of being a practice that is over 30 years old is that we have contacts in many fields to help clients get where they need to go, because sometimes chiropractic, as wonderful as it is not the answer. But I bet we can find someone for you who is.
So next time you get adjusted, pay attention to how you feel, do you feel more relaxed? More alert? Sharper? Freer? We’d love to hear about what you find.
Still working from home? How to keep your Neck and shoulders moving
Even though Melbourne will be thawing out of Lock down 4.0, we are aware that a lot of our clients will still be working from home again for a while.
If this is you, Its very important that you keep on top of your spinal health while you re adjust to working from home for the foreseeable future.
Fortunately, during Lockdown 2.0, Martin made this comprehensive video outlining everything you can do to keep yourself moving stay on top of your posture, and free up a lot of the tension you have felt building, especially over the last few weeks of lock downs.
Avid readers of this blog will note that we posted this video in September last year, but given recent events, I feel like Martin’s video couldn’t be more poignant so I am reposting for your convenience.
If you have a specific issue please do not hesitate to contact the practice so we can see how we can keep you going.
As usual with our videos, the transcript is available below, but I strongly recommend you have a watch as Martin runs through some excellent tips, stretches, exercises and muscle releases that will have you feeling a lot more yourself during this period.
The video has a few sections so if you REALLY felt like it you can skip to a section you find most relevant, however the way that Martin has filmed it the segments build on each other to get the most out of each one.
Enjoy!
2:00 Todays video is about...
3:52- Where to begin?
4:15 Rotational Movements of the Neck
5:32 Lateral Flexion of the Neck
7:12 Flexion/ Extension of the Neck
8:07 Shoulder Exercise
9:28- 3 exercises to open shoulders
13:48- Overhead position for shoulders
14:54- Focus on Alignment
17:23- Intro Spikey Ball Exercise
18:27 Beginning of Spikey Ball Exercise
23:27 Conclusion
Hi, Martin here from Align Chiropractic. Today's video is a follow along video, meaning I'm going to be taking you through some things that you can do, and you can more or less just watch the video and follow on.
So, the purpose of this video, it's really about moving your upper spine, your neck, your shoulders, your middle back to get mobility in those areas but also to soothe those areas.
It's really based on the clinical model that we use in our practice where we see that there's a real benefit in looking at the spine in kind of a sequential way, that spinal problems generally what's happening is that segments of the spine rather than having the ability to move through their full range of motion and kind of jammed up from either trauma, or long periods of time in particular postures, or stress tightening up the muscles around it.
And then as the joints jam up that changes the way the nerves and muscles and all the other soft tissues work, which then changes the alignment of your spine, and this change in movement and alignment of the vertebra causes misfiring of nerves which has a whole range of effects on your body, but specifically it can affect your ability to kind of balance the whole system.
If you're not balancing the whole system then your spine's going to be less stable. It's much more common for you to have problems with your back, your neck and the rest of your body if things aren't stable. So, if we look at that it goes movement, then alignment, then balance, then stability and so a common thing that I’ll see is people talking about ‘I need to do stability work or core stability work’.
I actually think it's really important that we do the basics first we've got to get movement happening first, and then once we've got movement, then we want to have a proper alignment so that when we're stabilizing first of all it's more effective, but we're also locking in a good movement pattern and a good alignment pattern rather than locking in poor ones.
2:00 TODAYS VIDEO IS ABOUT...
So this one specifically, today's video is really about dealing with this upper part of the spine because many of us are locked into these postures working at a desk or the effect of stress tightens up our neck and shoulder muscles and pushes our head posture forward and so this is really about restoring movement to those areas and then getting our alignment back into that nice upright posture.
I'm also going to be combining some approaches that come from new research into the interplay between how we breathe and our stress response and in particular if you want to dive deeper into this, there's a neuroscientist called Andrew Hubermann who's based at University of California, sorry based at Stanford and we're going to be using a couple of different approaches to breathing that we're combining with the movement approach and using a ball- spikey ball, or a tennis ball, or a lacrosse ball that we'll be using to just release muscle tension and some of that will be just I'll be cueing you to breathe in through your nose, and then we'll also be using an approach called a physiological sigh, which is really where you just take in a deep breath through your nose and then another deep breath through your nose before
letting it out and the emerging evidence is that this is a really quick and easy way of us helping to unwind some of the neurological effects of stress which we know can have really significant impacts on how we feel and how healthy we are. So, let's dive straight into this follow along routine to help release tension in neck, shoulders, upper back, and get movement into those areas so that you can have a healthier, happier, more active body
3:52- WHERE TO BEGIN?
Well the first thing that we want to do is we want to encourage movement back into the neck, so with the postures that we've been in and the lack of movement and there's a tendency for our neck to kind of stiffen up, and there's a segmental part of that which is what wewould address in office with an adjustment, then there's kind of an overall regional movement that we can address with exercise.
4:15 ROTATIONAL MOVEMENTS OF THE NECK
So first movement we're going to do is we're going to be doing rotational movements. With this I just want you to be taking nice slow breaths, in through the nose, out through the mouth.
So first of all just turn your head all the way to the left, and then go all the way to the right. I'm going to go through this five times each way, and we're not pushing we're just holding at that end range- nice and gently.
Let's see it just easing into it letting your shoulders drop, just letting that tension, that sort of habitual tension ease away. That's it. I think that's four, probably need a better way to count to be able to do this. Okay, I'm going to say that's five.
5:32 LATERAL FLEXION OF THE NECK
So next we're going be moving into lateral flexion so we just need to be cautious with this, if you get any pinching, any sort of sharp sensation that says you don't want to go that far, you want to stop before that point.
All of these mobility things are done within what feels just you're touching that point of tension or restriction. So sideways it's going all the way over there.
I'm just pausing at that end range, maybe a count of three. Just working our way into that range, just getting every vertebrae in our neck and even into our upper back starting to move.
This is our third one. Maybe just pause a little bit longer there, any sort of knotty points you can just almost sort of focus on it, just get that movement happening, just nodding a little bit back and forward. Okay that's four. So one more to go.
Last round for lateral flexion. Lateral flexion's actually a really important movement there's not many day-to-day activities that we do to encourage this range of motion, so it's often an exercise that we'll have people do because getting lateral flexion actually encourages movement in the other range.
7:12 FLEXION/ EXTENSION OF THE NECK
So now we're going to go flexion/ Extension. Flexion I'm going to get you to go nice and gently on, because we all tend to spend a lot more time in flexion than we do an extension. With extension which is the one going back, again just be really mindful that you don'twant to be getting any pinching sensation with that. With this one I'm doing it up against the wall. If you feel any dizziness with this then back off, maybe skip this part of it. This is our last one, our fifth repetition. Okay.
8:07 SHOULDER EXERCISE
Now functionally interlinked with your neck is your shoulders, and so again all this time spent like this, there's an alignment component of that, but before we can really address the alignment we've got to get the ability for these joints to move, so first up I’m going to do a stretch across the body, trying not to mess up my mic here.
So come all the way across, and we're just going to breathe in through the nose, and out. I'm going to do this one for three breaths. Just going to go a little bit further on this third one. Okay and then we're going to swap our arms. Bringing the arm across, the other arm just hooks in next to the elbow there. Breathe in, out. Breathe in, and out.
9:28- 3 EXERCISES TO OPEN SHOULDERS
So, it started to get some mobility, but really if we want to be able to bring our shoulders back which is what most of us need because so much of our activity is in front of us, we want to be opening up and restoring that movement that way.
So what we're going to do here is spend sort of three exercises bringing and opening up this in the front of our shoulder.
The first one what we're going to do here is we're going to put our hand up on the wall above horizontal, so if that's horizontal first one we want is up here, and then i've got my body sort of facing away there my elbow is straight, and then i'm turning out this way, and then i'm going to do three breaths there. So in through the nose, and out. That’s two. I can just rotate a little bit more, and three.
I'm just going to take that tension off, and now i'm going to that horizontal level, and it'll feel a little bit different, it's going to hit a slightly different part of the shoulder.
So again in through the nose, and out through the mouth. And three. Now we're just going to do just below horizontal to again getslightly different part of the shoulder.
We're going to come across. One, Two, that’s three. Okay, so now we're going to repeat exactly the same thing but on the opposite side. So first one, if that's horizontal we're going up maybe 30 degrees above horizontal, rotating away feeling the stretch at the front of the shoulder maybe a little bit into the arm. One, Two, That's three.
Then we're going to a horizontal point now, taking that stretch back up, and then in through the nose, out through the mouth. That's three. So, I'm going to get out just below horizontal one there, take that stretch up. And then in through the nose, and out. Then that's it, just move your shoulders around enjoy that extra mobility there.
13:48- OVERHEAD POSITION FOR SHOULDERS
So next what we're going to be working on is bringing up into flexion or sort of like an overhead position for our shoulders. So, with this I'm standing sort of basically like arm length away from a wall, and I reach out, I put my hands down keeping my elbows straight and then what i'm doing from here is keeping my arms straight and dropping my body all the way down.
I'm not rounding my back, I'm keeping my back quite straight, and then getting that movement back into the shoulders giving them that full range. We're just going to do three breaths here, so in through the nose and then out.
14:54- FOCUS ON ALIGNMENT
So next what we're going to do is move on from looking at movement and we're going to focus instead on alignment. What we're really wanting to do is to reverse that tendency that we all have to have this sort of position, and so what we're going to do is do an exercise called a W exercise, which is where you make your arms into a W shape with the thumbs facing backward.
I always like to sort of correct the head posture so pull your head back, and I also like to look up slightly because that helps just release the activation here. What we're really wanting to do is use these muscles down here in between our shoulder blades. So, make the W shape look up slightly and then what we're doing is trying to not use these muscles but use those ones in between your shoulder blades.
We're squeezing back one two three. Relaxing one, two, three. One, two, three. One two, three. We're going to go for ten so that's four, three. One, two, three, so I'm going to say that one's four, and five
Six. If it's getting uncomfortable, if things are starting to burn just take a little break, six and seven.
So it's kind of this back and down movement that we're after- just caught myself looking down too much. Nine and last one. Good.
What we've done there is really kind of reset our alignment, and that'll mean that rather than when your heads forward everything through has to be working overtime just to stop your head from going forward with gravity. So we're going to use that we've gotmovement, we've got alignment.
SPIKEY BALL: 17:23
Now what I want to do is just kind of soothe this area. We're all doing a lot of this, let's just work through with some pressure on those areas, and for this i'm going to suggest that you use a ball, a spiky ball. In this case this is a lacrosse ball, and what we're going to start with is we're going to be doing three individual spots. We're going to be doing one right in between the spine and the shoulder blade here, then we're going to be doing one that's up, almost on the meaty bit above your shoulder blade, and then we're going to be doing this little corner in here where your arm joins onto your shoulder blade there.
We're going to do that on each side. We're going to use that slightly different breathing where rather than just breathing in through your nose and then out through your mouth, if you want to experiment with it, this is a really good place to use that physiological sigh, which just helps reset our nervous system from a stress sort of state, into what they call a parasympathetic state, which is putting your nervous system in a state to promote rest and relaxation and kind of de-stressing.
18:27 BEGINNING OF SPIKEY BALL EXERCISE
So let's start off. You put the ball against the wall, and then just drop it down a little bit so you can get into that spot and rather than rolling around, what I like to do for this is just find a tender spot, hold pressure there. And then we're going to go breathe in through the nose, and then second breath, and then out. So just moving into a slightly different spot there.
Breathe in, second breath, and out. Breathe in.
Now we're going to move to the top of the shoulder. So, for this one you almost need to angle back a little bit. I'm just going to find that fleshy bit there. All right so I’m going to breathe in. Okay, so that's our three breaths there. Now for this one, I've got a really a choice of going on the actual arm here, or for most people this area in the side of the shoulder blades the spot that you want to hit, so I'm going to hit that one.
If you're doing this by yourself you could maybe do an extra round where you go to the other one if you're feeling tender in both, but I'm on the side of the shoulder blade.
The easiest way of getting there is having your body sort of on a 45-degree angle there, just finding that tender spot- okay that's definitely it. And so I'm going to breathe in through my nose, that's number two, let's go for number three- that's a really tender one.
Okay, so now what we're going to do- oops dropped my ball. And i'm back. All right so same sequence, we're just going to do the opposite side. So again, ball against the wall, I'm just going to roll into that spot just next to my shoulder blade there. All right that's it, I've got the right spot, so I'm going to breathe in through my nose. Second breath.
So now I'm just going to reposition that ball. I'm getting ready from the top of that shoulder blade there. First breath, double breath. Second breath, that's our third breath there.
Now we're just going to move to the outside of the shoulder there. So again, looking for either on the shoulder blade or the back of the arm. So I'm going to keep it consistent that 45 degree angle here. I’m going for that spot on the shoulder blade just breathing in I'm just moving up a little bit, finding that real epicenter of tension there. All right that's it, so breathe in at that spot...really relax into it. One more, breathe in through the nose.
CONCLUSION: 23:27
So there we have it, we've got movement through shoulders, neck, sort of upper back as well, then we've reset our alignment so thatwe're in a nice upright position and then we've kind of reset the tension, reset the nervous system giving you the best chance of having ahealthier, happier more active body. Thanks for following along.